

As the supply of slaves dwindled between the fifth and eighth centuries, a new class emerged from the combination of free peasants and slaves, the serfs.
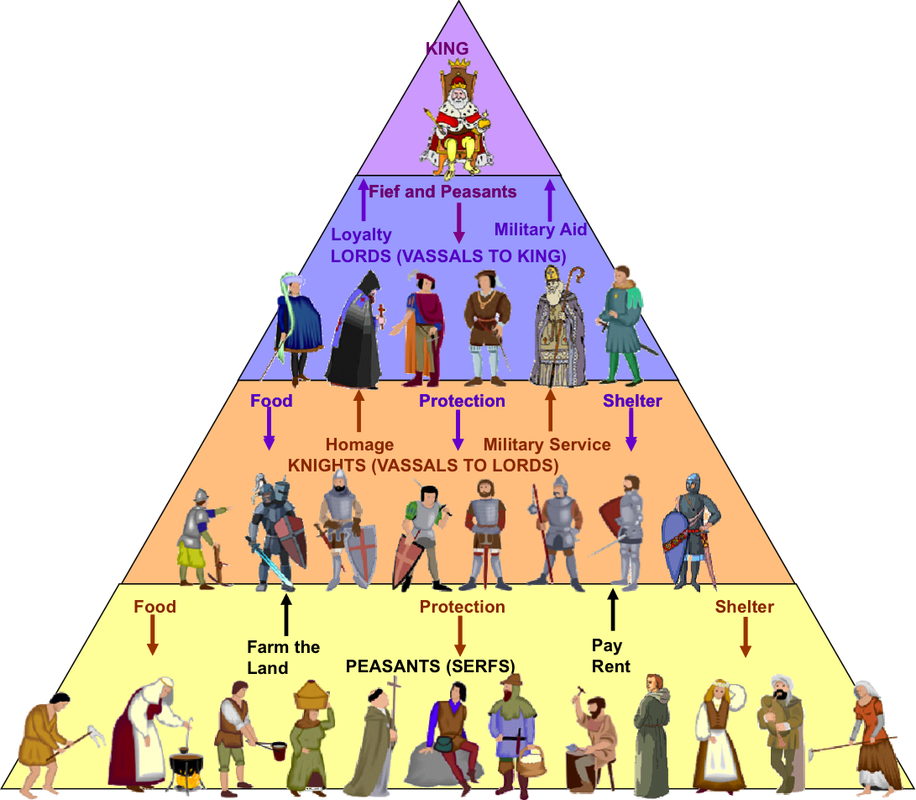
In the Roman villa, gangs of slaves worked the land of the owner. In the manorial system, however, the bonds were between lords and serfs and were defined by conditions of protection, labour and economic support. However, relationships between the nobility and the peasantry, manorialism, reflect a similar power structure.ĭeveloping from the Roman villas of late antiquity, the manor became the basic agricultural unit in the early Middle Ages and reflected the system of personal bonds seen in feudal arrangements. Use of the term feudalism is typically restricted to the relationships between members of the nobility. To deal with the potential for conflicting loyalties that subinfeudation could create, documents were often written to outline the precedence of the various lords by which a vassal may be bound, defining a single overlord as liege lord.Īll feudal relationships were based on a perceived, if not an actual, imbalance of power and the mutual exchange of goods, lands or services. This condition, called subinfeudation, illustrates the amazing complexity and flexibility of feudal institutions. Depending on the lands that a man held, he could be vassal to more than one lord and lord to more than one vassal. The structure of these feudal arrangements was fluid and cannot be forced into a defined hierarchy. Over time, these land grants became hereditary and ownership of the land seldom reverted back to the lord, except in cases of Technically, ownership of the land remained with the lord but the vassal received "use of the fruits", or usufruct, in exchange forįealty to the lord. The vassalage agreement was between the owner of the fief, the lord, and the recipient of the fief, the The basic unit of these feudal arrangements was the fief, a section of land granted for temporary use. Noble bishops and abbots increased the prestige and political clout of their natal families while the presence of a royal member within a monastery benefited the entire spiritual family.įeudalism is the term applied to relationships between members of the aristocracy. This tied the Church into the feudal network as family loyalties remained intact for clergy and the hierarchy of the Church mirrored the social structure of a patriarchal secular society. In the Middle Ages, one of the most common paths for younger siblings was to enter into ecclesiastical service.
#TIME FRAME FEUDALISM IN THE MIDDLE AGES FULL#
Under this law, the eldest son received the full inheritance of the father, leaving younger sons to make their own way. In order to prevent the splintering of family property, the law of primogeniture was adopted across most of Europe. Family alliances of blood and marriage were utilised to strengthen feudal ties and to increase power bases.

Functioning as a form of social security, the family provided protection and care to the children, the aged and infirm. Nevertheless, by the late Middle Ages, the terminology and concepts that are implied in the designation of a feudal society had been defined by the legal profession and can be applied to the time period of this tutorial.īook Reviews of "Fiefs and Vassals" by Susan Reynoldsįor noble and peasant alike, the family was the single most important social unit of the Middle Ages and the basis for other relationships. How these agreements developed and how they were utilised during the early Middle Ages are currently topics of scholarly debate. In the Middle Ages, networks of personal agreements formed the basis of the political, economic and social systems. End of Europe's Middle Ages - Feudal Institutions


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
